On this week’s show– Laserbones–Chris and Cameron discuss laser-3-D-Printed materials based on bones (lasers & bones), the use of cremated remains for synthetic diamonds (bones), and potential space mirror technologies made out of laser-trapped polystyrene beads (lasers)! We also have our first iTunes review!
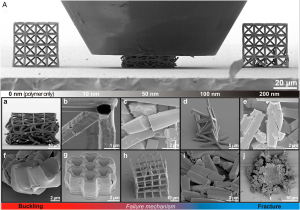
Compression tests on 3-d printed micro structures (source)
3:23 Article from The conversation.com titled “Scientists create bone-like material that is lighter than water but as strong as steel”
3:45 The paper was published in PNAS and is titled “High strength cellular composites with 3-D microarchitecture”
9:00 the structure of these materials are 3-d laser printed plastic that is then coated with Alumina (Al2O3).
14:00 what would you do instead of building structures out of this material? Chris would build indestructible bees.
15:00 how laser-sintered 3-d printing works (this is kind of cool)
19:50 we begin on a story inspired by an NPR piece, “From Ashes To Ashes To Diamonds: A Way To Treasure The Dead” where a swiss company will take cremated remains and turn them into a diamond for you.
22:30 we talk about what dopants are used to color Al2O3 crystals like sapphire and ruby (we call the clear Al2O3 “sapphire” in the lab, but most people just know sapphire as the blue gem).
24:50 The materials science aspect of the topic, how synthetic diamonds are grown!
26:45 Oh no! we forgot to explain what a phase diagram was! check this out in the meantime https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phase_diagram
28:00 for reference, the melting point of some steel is near 1500 C, which is much less than the 3000 C needed to form graphite with a direct transition (no catalyst or seed material)
29:00 just the CVD process for growing Diamond was patented by Apollo Diamond, not the CVD process in general, this is a very common technique!
32:16 newscientist.com “Laser light makes ultra-light mirror out of tiny beads” and the accompanying paper:
“optical mirror from laser-trapped mesoscopic particles.”
34:09 Chris has an interesting story about mirrors used in solar cells! (you put one at the back, and it helps make solar cells collect more light and be more efficient)
36:25 back on topic! they want to use laser-trapped polystyrene beads to create mirrors that are very light and useful for space telescope.
39:30 they are slightly “cheating” by holding the beads against a glass slide, and they are holding the whole thing underwater to help with cooling the beads and to help stabilize them
47:10 our very first listener feedback segment!!! Thanks!
48:30 and our very first correction!
Intro: Open – Crying (Get Olde)
Baby Bones – Laura Stevenson and the Cans
Diamond Rings – Fake Problems
Black Mirror – Arcade Fire
Outro: Dreams are Maps – The Wild (Dreams are Maps)
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | RSS








Recent Comments